Conservation strategies

Source: https://uwaterloo.ca/off-campus-housing/blog/post/think-green-think-greener
Conservation, waste reduction and recycling
The Three R's
Reduce, Reuse and Recycle is commitment towards E waste cleanup, increase corporate social responsibility and commitment for the reduction of C02 emissions. This Reduce, Reuse and recycle and commitment is also known as the three R’s initiative and this commitment for now and the future.The three R’s – reduce, reuse and recycle – all help to cut down on the amount of waste we throw away. They conserve natural resources, landfill space and energy. Plus, the three R’s save land and money communities must use to dispose of waste in landfills. Siting a new landfill has become difficult and more expensive due to environmental regulations and public opposition.
Reduce: means to reduce consumption and the amount of waste generated. This includes buying and consuming less, as such also throwing away less.Reduce the amount of waste we produce in the best way possible so as to help the environment. Reducing consumption and waste production is the first and most effective step toward producing less waste (consuming less automatically produces less waste). However, there are times when consumption is necessary. In these cases, reuse as much as possible before recycling any remaining materials.
Reuse: ” is simply the act of using an item again and again in its original form. Reusing items eliminates the need to reprocess materials (whether it is for disposal, or for recycling). find ways to reuse already produced goods and products instead of producing new and imposing on the environment
Recycle: means to give old or used things a new lease of life, by making new things out of the old materials. recycle as much as possible from the waste that goes out of the house, the restaurant, the company, the community and the factory.
Source: http://ewastecleanup.com/the-three-rs-reduce-reuse-recycle-facts-and-statistics/
Examples of how to put the three R's into practice
Reduce: reducing the amount of waste you produce is the best way to help the environment. There are lots of ways to do this. For example:
- Buy products that don’t have a lot of packaging. Some products are wrapped in many layers of plastic and paperboard even though they don’t need to be. You can also look for things that are packed in materials that don’t require a lot of energy or resources to produce. Some products will put that information right on their labels.
- Instead of buying something you’re not going to use very often, see if you can borrow it from someone you know.
- Cars use up energy and cause pollution. Some ways to reduce the environmental damage caused by cars include carpooling with friends, walking, taking the bus, or riding your bike instead of driving.
- Start a compost bin. Some people set aside a place in their yard where they can dispose of certain food and plant materials. Over time, the materials will break down through a natural process called decomposition. The compost is good for the soil in your yard and means that less garbage will go to the landfill.
- You can reduce waste by using a computer! Many newspapers and magazines are online now. Instead of buying the paper versions, you can find them on the Internet. Also remember that you should print out only what you need. Everything you print that you don’t really need is a waste of paper.
- Save energy by turning off lights that you are not using.
- Save water by turning off the faucet while you brush your teeth.
- Lots of families receive a large amount of advertisements and other junk mail that they do not want. You can stop the mailings and reduce waste by contacting the mailing service and requesting that they take your name off of their distribution list.
Reuse: instead of throwing things away, try to find ways to use them again! For example:
- Bring cloth sacks to the store with you instead of taking home new paper or plastic bags. You can use these sacks again and again. You’ll be saving some trees!
- Plastic containers and reusable lunch bags are great ways to take your lunch to school without creating waste.
- Coffee cans, shoe boxes, margarine containers, and other types of containers people throw away can be used to store things or can become fun arts and crafts projects. Use your imagination!
- Don’t throw out clothes, toys, furniture, and other things that you don’t want anymore. Somebody else can probably use them. You can bring them to a center that collects donations, give them to friends, or even have a yard sale.
- Use all writing paper on both sides.
- Use paper grocery bags to make book covers rather than buying new ones.
- Use silverware and dishes instead of disposable plastic utensils and plates.
- Store food in reusable plastic containers.
Recycle: Many of the things we use every day, like paper bags, soda cans, and milk cartons, are made out of materials that can be recycled. Recycled items are put through a process that makes it possible to create new products out of the materials from the old ones.
In addition to recycling the things you buy, you can help the environment by buying products that contain recycled materials. Many brands of paper towels, garbage bags, greeting cards, and toilet paper, to name a few examples, will tell you on their labels if they are made from recycled materials.
In some towns you can leave your recyclables in bins outside your home, and a truck will come and collect them regularly. Other towns have recycling centers where you can drop off the materials you’ve collected. Things like paper and plastic grocery bags, and plastic and aluminum cans and bottles can often be brought to the grocery store for recycling. Whatever your system is, it’s important to remember to rinse out and sort your recyclables!
Source: http://ecogreendog.com/the-three-rs/
Substitution
Substitution is the replacement of a substance, process, product or service by another that maintains the same functionality. Substitution should aim over the whole life cycle of the replacement to obviate any negative impacts on human health or the environment and improve resource efficiency.
Source: https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/227031/Forum-guide-substitution-101105.pdf



Source: http://www.slideshare.net/gabr0088/recycling-and-substitution
Reducing consuption of carbon fossil fuels
The release of carbon into the atmosphere can enhance the greenhouse effect, causing global warming along with associated side effects e.g. rising sea levels, climate refugees, increased frequency and magnitude of tropical storms and desertification (see Atmosphere and change for more details).
The creation of electricity using fossil fuels (oil, gas and coal) releases the most carbon, but industry and transport are also significant releases of carbon. Domestically we can influence the release of carbon by our demand for electricity i.e. if we use more electricity more carbon will be released.
In overall terms, China releases the most carbon, closely followed by the US. If you look at a per capita level, then some of the Gulf States (Qatar, UAE and Kuwait) are the worse.
The graph shows the world's top carbon producers in overall terms, the table below (left) shows the top carbon producers per capita and the table below (right) shows the contributors to carbon production in Singapore.
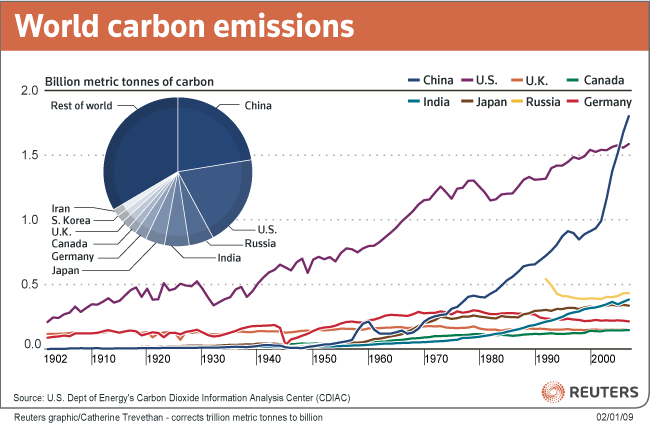
Source: http://greenfieldgeography.wikispaces.com/conservation+strategies
Follow the links below for more information:
List of ways to reduce consumption of fossil fuels
Conserve Energy
People can do simple things to decrease energy consumption. Energy consumption can be reduced by simply turning off lights when a room is not in use, replacing light bulbs with longer-lasting fluorescent bulbs and only running air conditioning when a home is occupied. Other steps to reduce fossil fuel reliance include ensuring your home has efficient insulation for heating and cooling purposes and using Energy Star-rated consumer appliances. The Energy Star label is awarded to efficient products that reduce the total amount of energy used and typically display a calculated year’s savings as a percentage or dollar amount to help inform consumers.
Reuse Products
Many consumer goods can be reused instead of discarded. For example, use a fabric grocery shopping bag instead of paper or plastic. Reusable glass plates and cups will also reduce the amount of Styrofoam and plastics that require fossil fuel resources. When shopping, you can also buy post-consumer manufactured goods made from recycled materials. Some products such as computer printer ink cartridges may also be refilled and reused.
Recycle Materials
The Environmental Protection Agency estimates that 75 percent of American waste is recyclable. You can help reduce the reliance on fossil fuels by recycling your waste instead of sending it to a landfill. Donate working products such as microwaves, lights, fans, clothing that no longer fits and household goods you no longer want to charities like Goodwill instead of throwing them away. It’s also a good idea to participate in your city’s recycling programs that provide trash bins for plastics, aluminum and paper.
Live Green
One solution to the depletion of nonrenewable fossil fuel usage is to go green. Going green means living your life in a way that sustains current resources for future generations. Green living always seeks to find a balance between humans and natural surroundings. This lifestyle choice focuses on respecting the environment by using as few resources as necessary; consuming only the food and energy needed for survival; participating in recycling programs that reduce municipal solid waste; using green energy electricity services such as solar power, which reduces pollution; and working together with other community members to ensure your children and grandchildren get to experience the same high-quality life. Communities can also go green by encouraging local lawmakers and planning agencies to create walkable neighborhoods where human interactions are favored over cars that pollute the air.
Source: http://education.seattlepi.com/list-ways-reduce-use-fossil-fuels-3725.html
Strategy for reducing fossil fuel consumption - Ethanol in Brazil
Ethanol: Sugarcane ethanol is an alcohol-based fuel produced by the fermentation of sugarcane juice and molasses. Because it is a clean, affordable and low-carbon biofuel, sugarcane ethanol has emerged as a leading renewable fuel for the transportation sector. Ethanol can be used two ways:
Blended with gasoline at levels ranging from 5 to 27 percent to reduce petroleum use, boost octane ratings and cut tailpipe emissions
Pure ethanol – a fuel made up of 85 to 100 percent ethanol depending on country specifications – can be used in specially designed engines
Benefits of Ethanol
- Cleaner Air. Ethanol adds oxygen to gasoline which helps reduce air pollution and harmful emissions in tailpipe exhaust.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Compared to gasoline, sugarcane ethanol cuts carbon dioxide emissions by 90 percent on average. That’s better than any other liquid biofuel produced today at commercial scale.
- Better Performance. Ethanol is a high-octane fuel that helps prevent engine knocking and generates more power in higher compression engines.
- Lower Petroleum Usage. Ethanol reduces global dependence on oil. Sugarcane ethanol is one more good option for diversifying energy supplies.
Brazil: A Leader in Ethanol Production and Use
Brazil has achieved greater energy security thanks to its focused commitment to developing a competitive sugarcane industry and making ethanol a key part of its energy mix. In fact, Brazil has replaced almost 42 percent of its gasoline needs with sugarcane ethanol – making gasoline the alternative fuel in the country. Many observers point to Brazil’s experience as a case study for other nations seeking to expand use of renewable fuels and have identified two key factors for success:
- Sugarcane Ethanol. Brazil is the world’s largest sugarcane ethanol producer and a pioneer in using ethanol as a motor fuel. In 2013/14, Brazilian ethanol production reached 27.5 billion liters (7.3 billion gallons). Most of this production is absorbed by the domestic market where it is sold as either pure ethanol fuel or blended with gasoline. All gasoline sold in Brazil includes a blend of 18 to 27 percent ethanol.
- Flex Fuel Vehicles. The country first began using ethanol in vehicles as early as the 1920s, and the trend gained urgency during the oil shock of the 1970s. However, sugarcane ethanol’s popularity really took off in 2003 with the introduction of flex fuel vehicles that run on either gasoline or pure ethanol. More than 90 percent of new cars sold today in Brazil are flex fuel due to consumer demand, and these vehicles now make up about half of the country’s entire light vehicle fleet – a remarkable accomplishment in less than a decade. As a result, Brazilian consumers have a choice at the pump when they fuel their cars and most are choosing sugarcane ethanol for its price and environmental benefits, making gasoline the alternative fuel in the country.
Since 2003, the combination of sugarcane ethanol and flex fuel vehicles has reduced Brazil’s emissions of carbon dioxide by more than 300 million tons. That’s as good for the environment as planting and maintaining 2.1 billion trees for 20 years!
Source: http://sugarcane.org/sugarcane-products/ethanol
Watch video and follow the links below for more input on ethanol in Brazil:
Pros and cons
Pros
- Truly a renewable fuel
- Widely available and naturally distributed
- Generally low cost inputs
- Abundant supply
- Can be domestically produced for energy independence
- Low carbon, cleaner than fossil fuels
- Can convert waste into energy, helping to deal with waste
Cons
- Energy intensive to produce. In some cases, with little or no net gain.
- Land utilization can be considerable. Can lead to deforestation.
- Requires water to grow
- Not totally clean when burned (NOx, soot, ash, CO, CO2)
- May compete directly with food production (e.g. corn, soy)
- Some fuels are seasonal
- Heavy feedstocks require energy to transport.
- Overall process can be expensive
- Some methane and CO2 are emitted during production
- Not easily scalable
Source: http://www.triplepundit.com/special/energy-options-pros-and-cons/biomass-energy-pros-cons/

No comments:
Post a Comment