Geopolitics of oceans
Sovereignty rights
UNCLOS
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea treaty, is the international agreement that resulted from the third United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS III), which took place between 1973 and 1982.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_Nations_Convention_on_the_Law_of_the_Sea
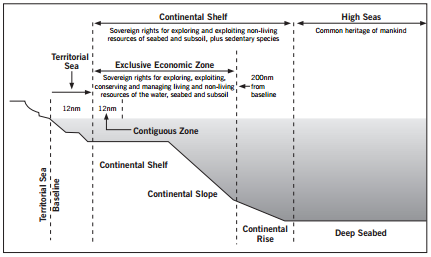
nm: Nautical mile - a unit used in measuring distances at sea, equal to approximately 2,025 yards (1,852 m).
Source: http://www.environmentguide.org.nz/issues/marine/marine-management/im:2075/
Territorial Sea
The territorial sea is an area of the sea that has an outer limit extending 12 nautical miles measured seaward from the baselines.
The coastal state has sovereign rights over the territorial sea. Its sovereignty extends to the airspace, seabed and subsoil. In this respect, the territorial sea is similar to a state’s land territory. Ships of all states enjoy the "right of innocent passage" through the territorial sea, but they must operate under certain conditions respecting international norms.
Contiguous Zone
The contiguous zone is an area of the sea adjacent to and beyond the territorial sea. Its outer limit measures 24 nautical miles from the normal baseline.
This band of sea is a buffer zone where the coastal state may exercise control to prevent infringement of its customs, fiscal, immigration or sanitary laws and regulations within its territory or territorial sea. The coastal state may also punish such infringements.
The contiguous zone is located within the first 12 nautical miles of the exclusive economic zone.
Exclusive Economic Zone
The exclusive economic zone (EEZ) is an area of the sea adjacent to and beyond the territorial sea, extending out to 200 nautical miles from the baselines.
Within the EEZ, a coastal state has sovereign and jurisdictional rights over exploration and management (e.g. scientific research and protection of the marine environment), and economic exploitation of living and non-living resources in the waters above the seabed, in the seabed and beneath the seabed.
Within the EEZ, states other than the coastal state enjoy certain freedoms, notably those related to navigation and flight.
Continental Shelf
The continental shelf of a coastal state comprises the seabed and subsoil of the submarine areas that extend beyond its territorial sea throughout the natural extension of its land territory to the outer edge of the continental margin, or to a distance of 200 nautical miles from the baselines, whichever distance is greater.
High Seas
The high seas is the area beyond the EEZ. No state has sovereignty or jurisdiction over the high seas. The UNCLOS specifically provides that no state may claim sovereignty over any area of the high seas.
International Seabed Authority
States that are parties to the UNCLOS manage the mineral resources of the area through the Authority. The prime objective of this agreement is sharing benefits derived from mining minerals from the area seabed. Royalties from mineral mining are paid to the Authority to distribute primarily to developing states. The Authority also distributes royalties paid for exploitation of non-living resources of the continental shelf beyond 200 nautical miles.
Source: http://www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/oceans/marinezones-zonesmarines/index-eng.html
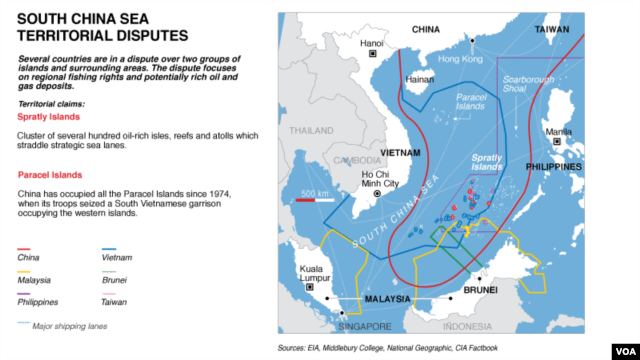
Conflict
Source: http://www.voanews.com/content/philippines-vietnam-agree-to-cooperate-on-resolving-maritime-dispute-with-china/1714462.html
Follow the link below for input on the South China Sea:

No comments:
Post a Comment